### Selector Angular have multiple ways to select the component (CSS-Selectors): - by element `
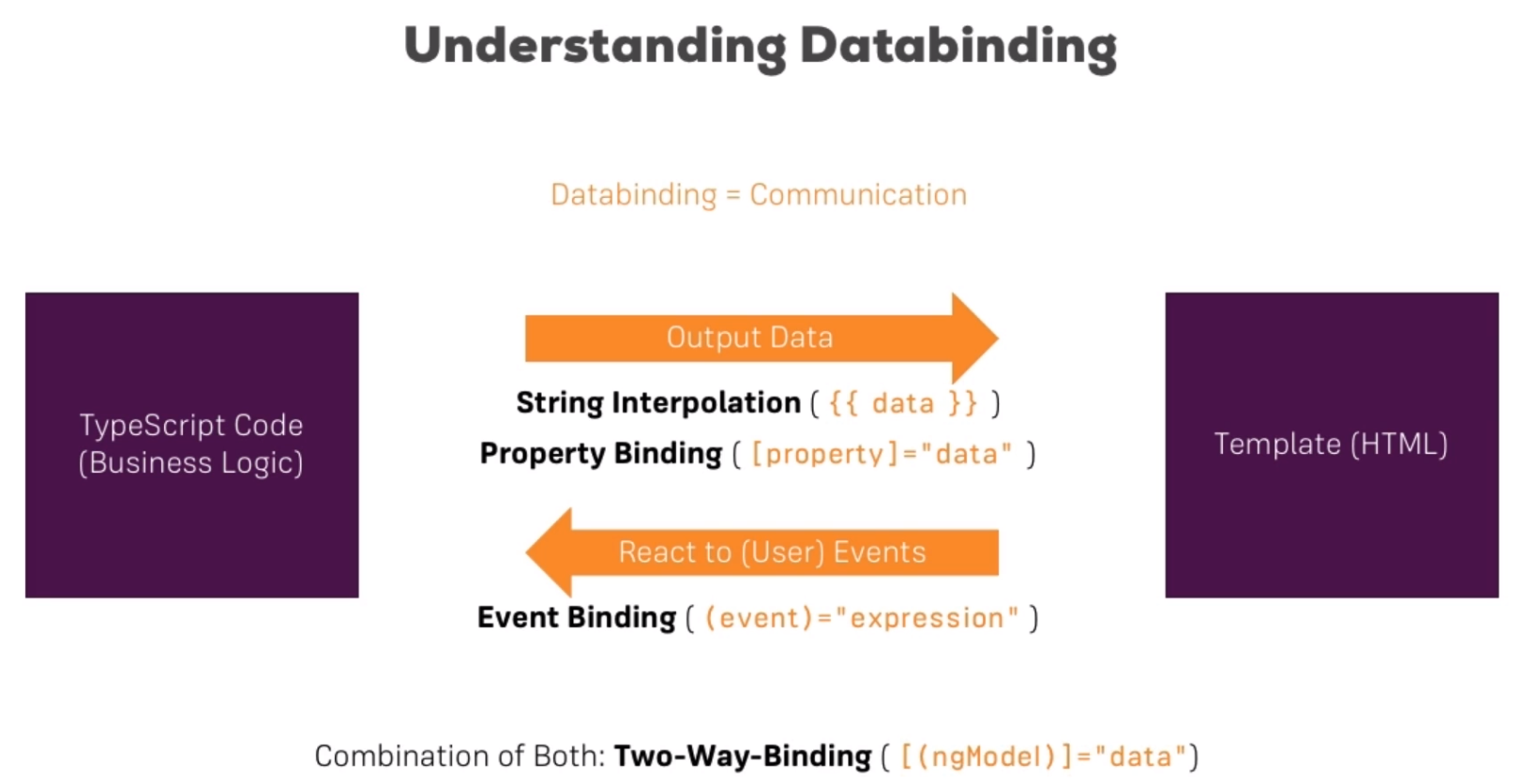
## String Interpolation With Databinding can be used to dynamically load data into the HTML-template. For example like this: ```html
{{ 'server' }} with ID {{ serverID }} is {{ serverStatus }}
``` In the `{{ }}` can be executed an TS Expression wich can be a simple property like `serverID`, `serverStatus` or any **Method** which returns a **string**. Note that a number can easily be converted into a string, so there is no need to explicitly convert it. The `{{ 'server' }}` is just a string output. **Useage:**To pront some text in the template use String interpolation. ## Property Binding `[ ]` indicates that we want to use a property binding. Exsample to activate a Button after 2seconds: servers.component.html ```ts ``` servers.component.ts ```ts export class ServerComponent implements OnInit { allowNewServer = false; constructor(){ setTimeout(() => { this.allowNewServer = true; }, 2000); } } ``` **Usage:**
Change something dynamically upon an element use Property Binding. ```html ``` This syntax is recognized by angular. You cant mix with the curlybraces from the string interpolation. String interpolation is a TS feature. ## Event binding **Syntax:** ```html (event)="methodeToCall()" ``` **Example:**
```html
{{ serverCreationStatus }}
``` ## Passing and Using Data with Event binding With the keyword `$event` we can extract lots of data from this object of type Event. server.component.ts ```ts ... onUpdateServerName(event: Event) { this.serverName = ({{ serverName }}
... ``` ## Two-Way-Databinding Important: For Two-Way-Binding to work, you need to enable the `ngModel` directive. This is done by adding the `FormsModule` to the `imports[]` array in the **AppModule**. You then also need to add the import from @angular/forms in the app.module.ts file: ```ts import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms'; ``` **Syntax:** ```html [(ngModel)]="" ``` Updates the Input or Target based on eather one is changed. ## Directives Directives are Instructions in the DOM.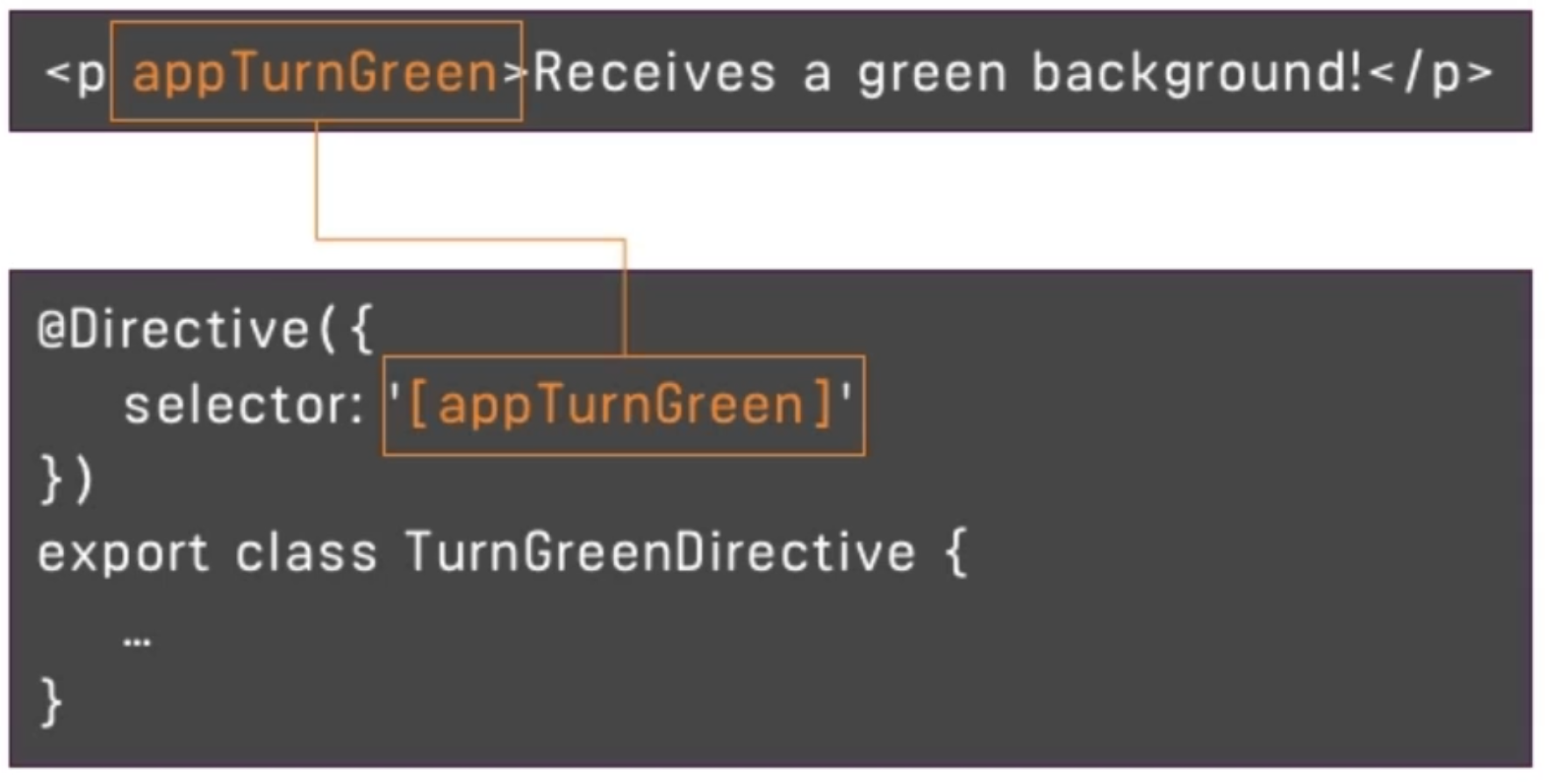
Angular Documentation of [Built-in directives](https://angular.io/guide/built-in-directives) ## ngIf Built-In directive which binds the data based on a condition. This ## ngStyle Changes a CSS style attribute ## ngClass Adds or removes a CSS-Class from the element. ## ngFor Adds an ammount of elements to the DOM. ```html
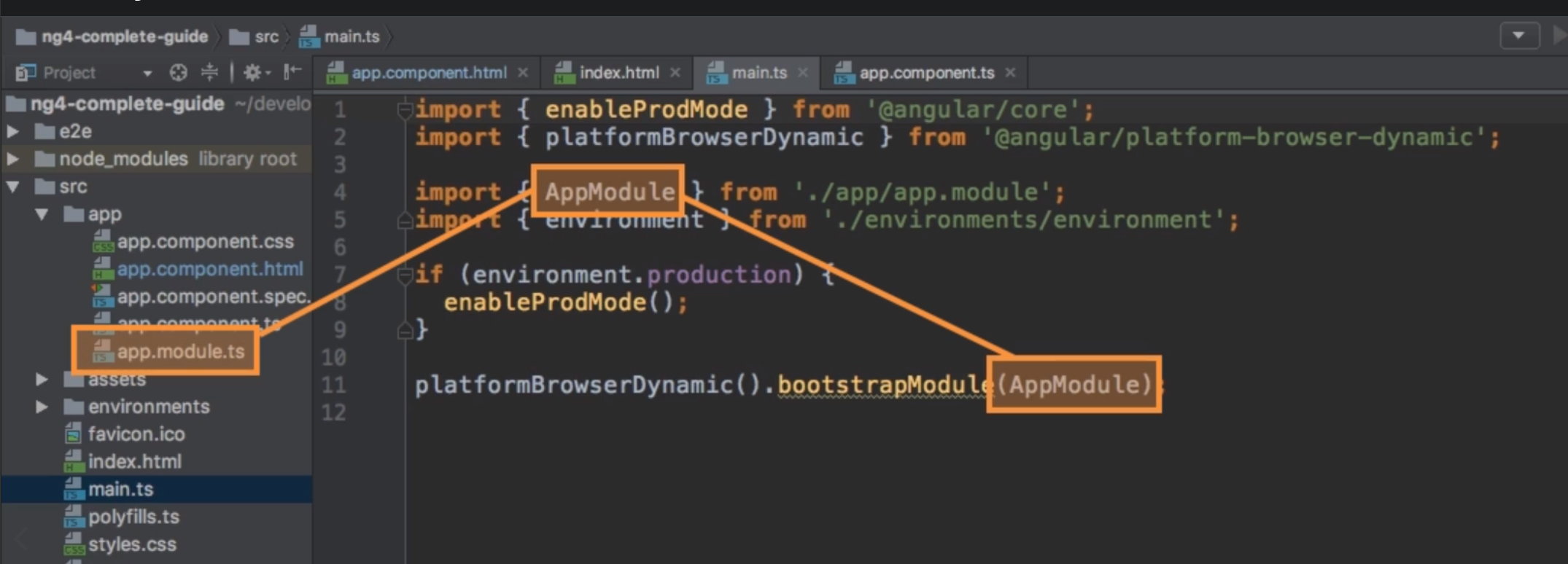
 Angular's main ideas is to build components to build an app. Each Component has it's own template (html), maybe it's own style (CSS) and more important it's own business logic.
Components can be reused in multiple parts or the application.
## Component
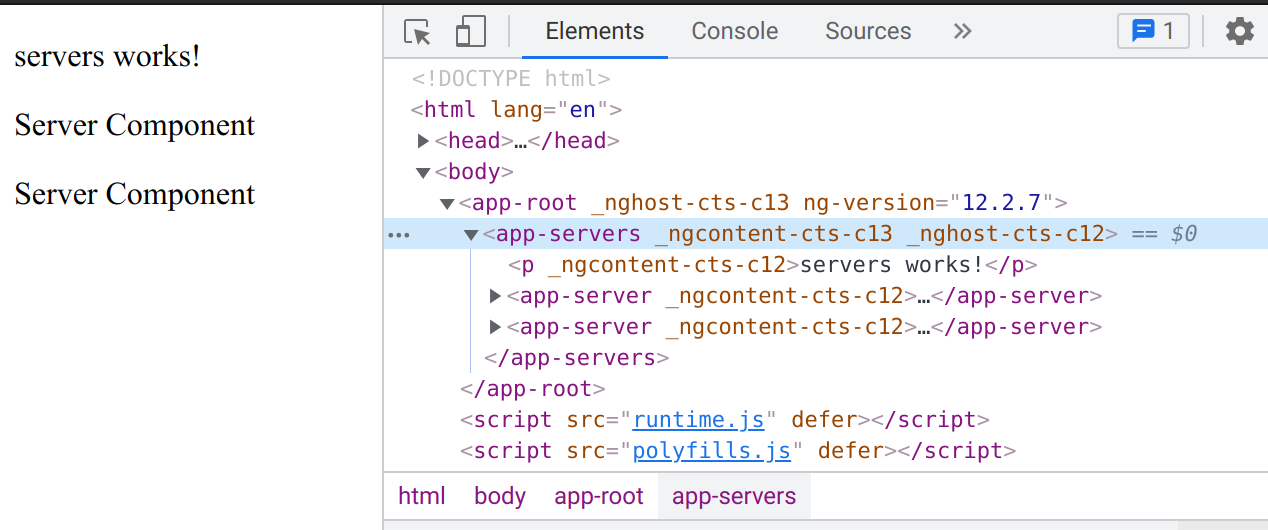
The `app.component` is a special component. It serves to bootstrap all the application and is the root of the application. All the *selectors* for the other components are located now in the `app.component.html`.
Good practice to create a new component, you should create a directory in the app folder and name it the same as the componentname. The convention of naming the component is like this `name.component.ts`.
A component is a class which angular is able to instanciate.
Required files for a component are a `server.component.ts` and a `server.component.html`.
In the *.ts file goes the logic and in the *.html file is the template of the component.
```ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core'; // Import for the Component-Decorator
@Component({ // Decorator
selector: 'app-server', // Unique selector
templateUrl: './server.component.html' // template file
})
export class ServerComponent { // Component-Class
}
```
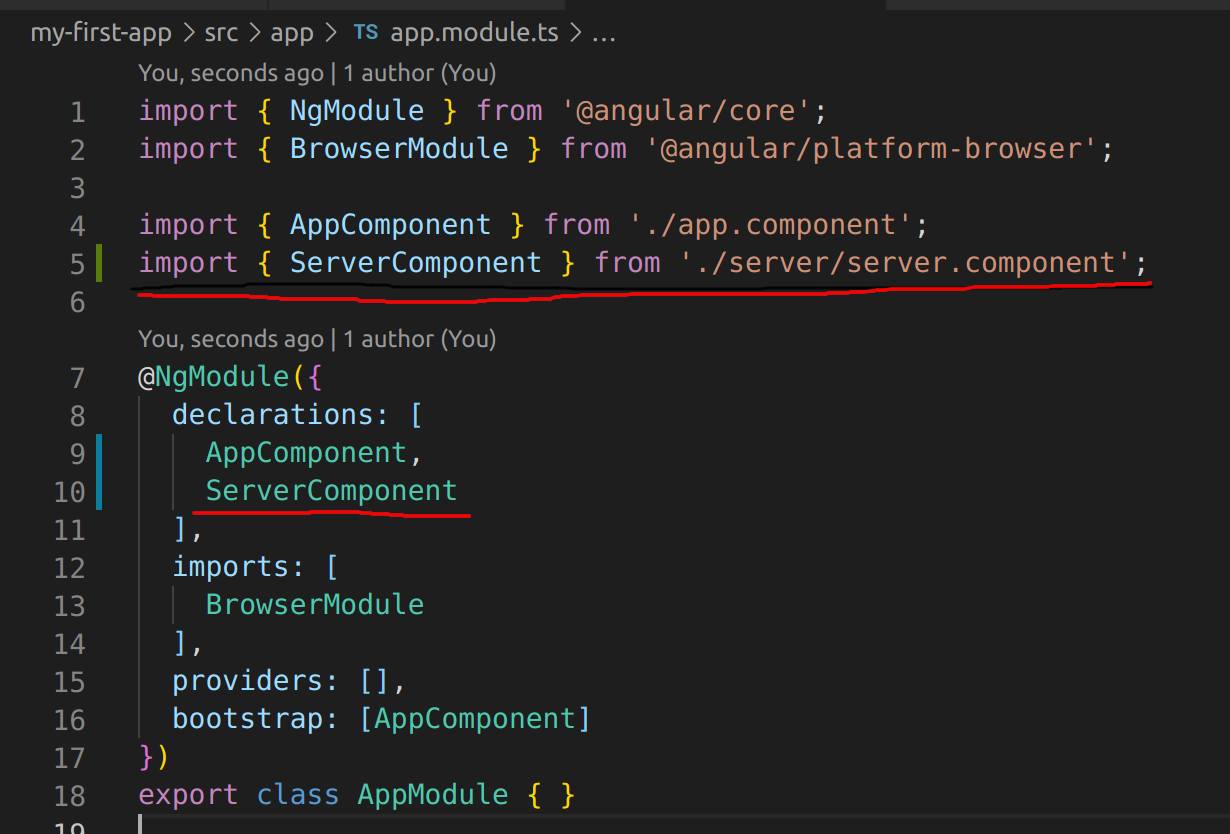
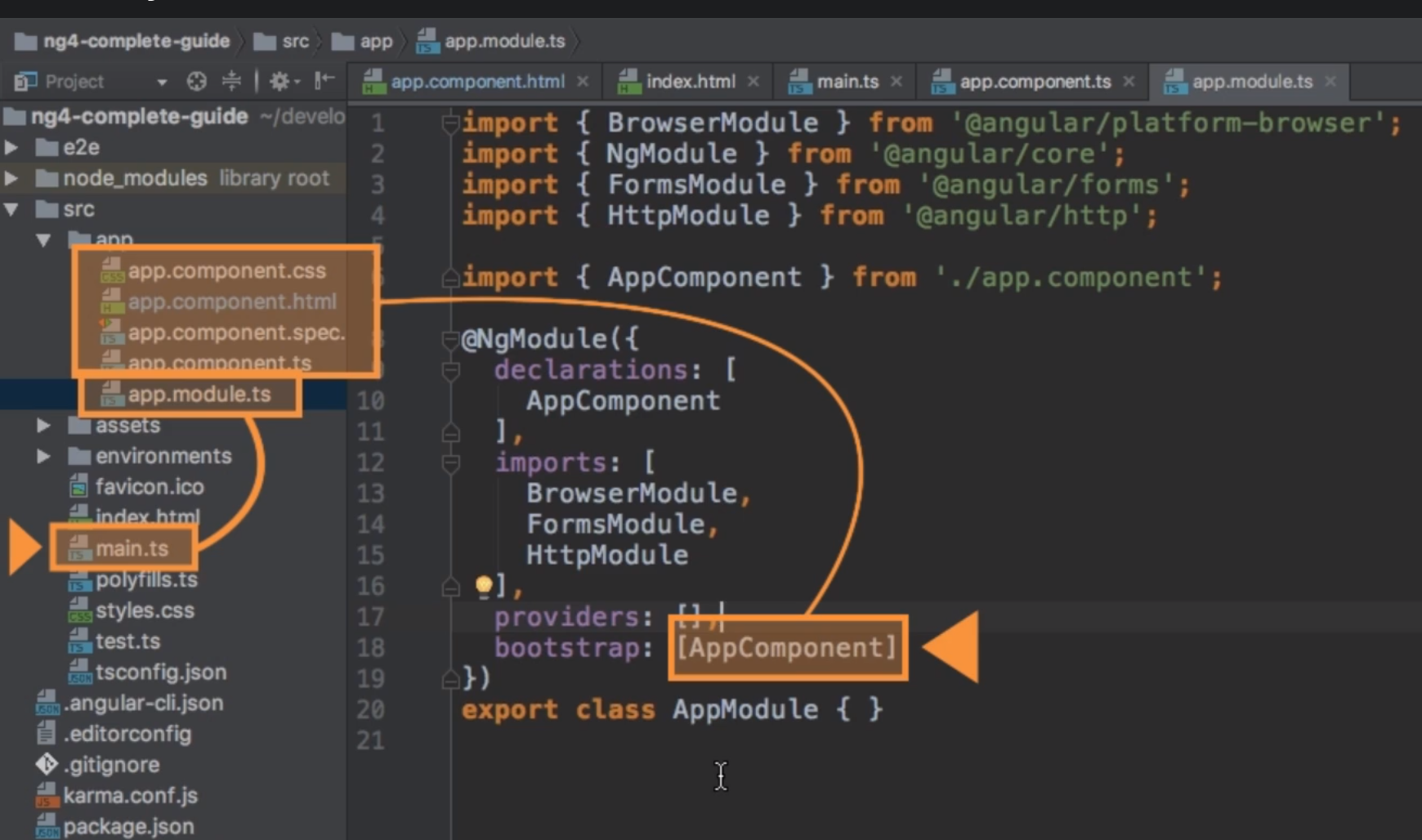
This register the component and let angular know that a new component was created, it needs to be declared in the root app module (`app.module.ts`). Add it in the `declarations`-array and for TS to find the file, it needs also an import.
Angular's main ideas is to build components to build an app. Each Component has it's own template (html), maybe it's own style (CSS) and more important it's own business logic.
Components can be reused in multiple parts or the application.
## Component
The `app.component` is a special component. It serves to bootstrap all the application and is the root of the application. All the *selectors* for the other components are located now in the `app.component.html`.
Good practice to create a new component, you should create a directory in the app folder and name it the same as the componentname. The convention of naming the component is like this `name.component.ts`.
A component is a class which angular is able to instanciate.
Required files for a component are a `server.component.ts` and a `server.component.html`.
In the *.ts file goes the logic and in the *.html file is the template of the component.
```ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core'; // Import for the Component-Decorator
@Component({ // Decorator
selector: 'app-server', // Unique selector
templateUrl: './server.component.html' // template file
})
export class ServerComponent { // Component-Class
}
```
This register the component and let angular know that a new component was created, it needs to be declared in the root app module (`app.module.ts`). Add it in the `declarations`-array and for TS to find the file, it needs also an import.